As the OpenStreetMap Foundation’s Senior Site Reliability Engineer (SRE), my focus in the OpenStreetMap Operations Team over the last year has been on driving efficiency, improving resiliency, and scaling our infrastructure to support the continued growth of the OpenStreetMap project. From cloud migration to server upgrades, we’ve made several improvements since last year to better position OpenStreetMap’s infrastructure to meet these resiliency and growth challenges.
Improving User Facing Services
Upgraded Rendering Services
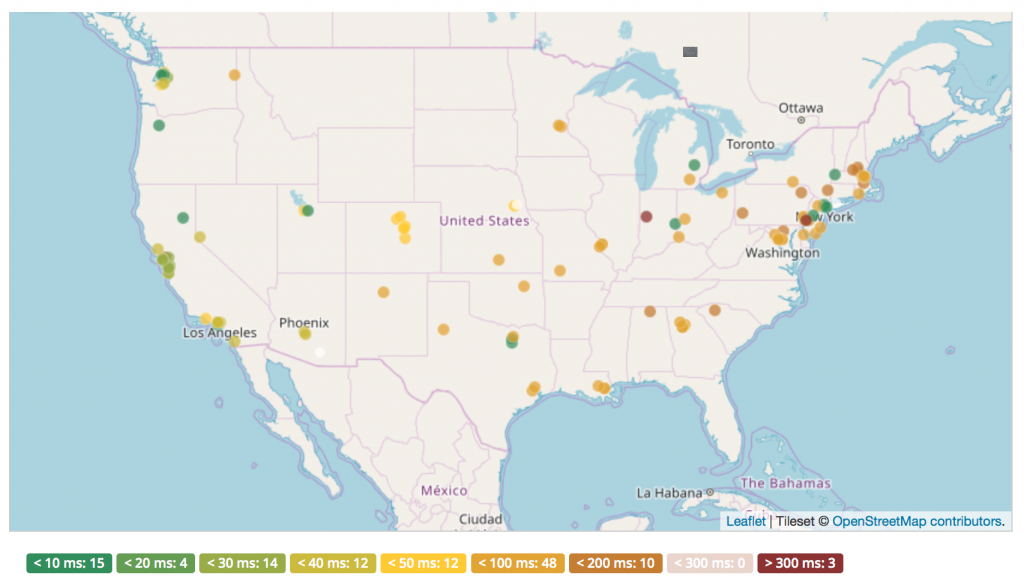
The tile rendering infrastructure saw notable upgrades, including hardware and software optimisations, faster tile cache expiry to address vandalism, and automation to block non-attributing users. We now re-render low-zoom tiles daily, improving both performance and allowing a faster mapper feedback loop. The tile service is widely used and keeping up with demand is an ongoing challenge.
New Aerial Imagery Service
Launched a new aerial imagery service that supports GeoTIFF COGs. The service now hosts aerial.openstreetmap.org.za which is backed by 16TB of high-resolution imagery. The new service makes it easier to host additional imagery in the future.
Transition to Gmail Alternative & Spam Mitigation
After facing significant spam issues with the OSMF’s Google Workspace, I migrated OSMF email services to mailbox.org. This has reduced the spam volume and improved administrative efficiency. We’re also in the process of transitioning historical OSMF Google Docs data to a self hosted service.
Dealing with DDoS Attacks and Vandalism
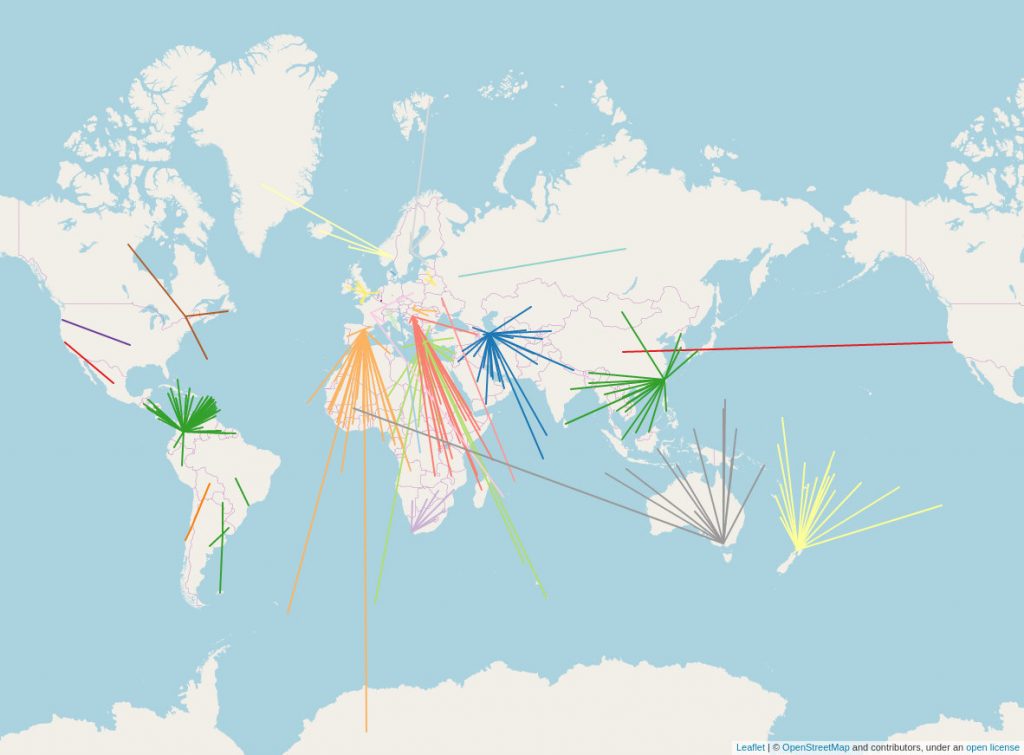
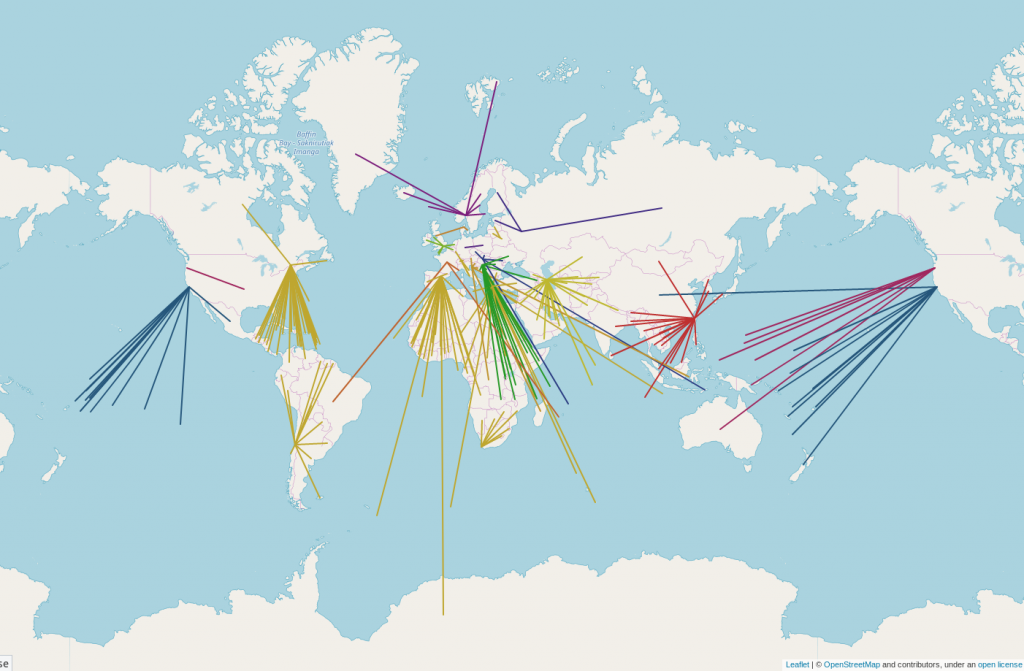
This year, we faced several Distributed Denial of Service (DDoS) attacks, including a major DDoS for ransom incident, which was reported to law enforcement. These attacks tested our infrastructure, but we’ve implemented measures to strengthen our resilience and better protect against future threats.
We also dealt with large-scale vandalism that affected OpenStreetMap services. Thanks to the swift response and adjustments made by the Operations team, we’ve reinforced our infrastructure to better handle abuse and ensure continuous service.
Planet Data Hosting on AWS S3
With the OpenStreetMap Operations Team I’ve moved our planet data hosting to AWS S3 with mirrors in both the EU and US, allowing us to fully reinstate the back catalog of historical data. Through AWS’s OpenData sponsorship, replication diffs and planet data are now more accessible.
Making Systems Easier to Manage
Full AWS Infrastructure Management Using OpenTofu
With the OpenStreetMap Operations Team I’ve successfully migrated all manually managed AWS resources to Infrastructure-as-Code (IAC) using OpenTofu (formerly Terraform). This transition allowed us to improve cost efficiency, enhance security by adopting a least privilege IAM model, and gain better visibility into expenditures through detailed billing tags. Additionally, we’ve integrated S3 Storage Analytics to further optimise our costs, set up additional backups, and implemented enhanced lifecycle rules.
Improved Service Outage Alerting
We implemented SMS-based alerting for critical service outages, alongside a sponsored PagerDuty account. These improvements ensure quicker response times and better coordination during outages, with full integration with Prometheus/Alertmanager and Statuscake in the works.
Technical Debt reduction
This year, we made progress in reducing technical debt by moving several legacy services to more maintainable solutions. For instance, we containerised old services, including legacy State of the Map websites that were previously running poorly maintained WordPress installations. This transition has improved the scalability, security, and long-term maintainability of these services.
Additionally, we replaced our custom source installation of OTRS with a Znuny package installation from Debian. This shift simplifies upgrades and reduces the maintenance burden, ensuring the system remains up to date and secure without custom modifications.
Ensuring Infrastructure Resilience Despite Hardware Failures
Over the past year, we’ve maintained a resilient infrastructure even in the face of hardware failures. We replaced numerous disks and RAM, ensuring minimal disruption to services. Our bespoke monitoring system allows us to detect early signs of hardware failure, enabling us to act quickly and replace faulty components before they cause significant issues. This proactive approach has been key to maintaining system uptime and reliability.
Upgrading Infrastructure
Cross-Site Replication of Backups
To ensure robust disaster recovery, I’ve established cross-account, cross-region replication for AWS S3 backups, enabling point-in-time recovery. This safeguards critical data and services, even in the face of major failures, providing long-term peace of mind.
High Availability Infrastructure
Key hardware upgrades in our Amsterdam, Dublin, and OSUOSL sites improved performance, storage capacity, and network reliability. New switches were installed in 2022, and we’ve now finished setting up a high availability (HA) configurations to ensure improved service, which we have continued improve the setup by moving to dual diverse uplinks to our ISP for better resilience.
Debian Migration
We are migrating from Ubuntu to Debian 12 (Bookworm) as our standard distribution. All new servers now run on Debian. Our chef configuration management has been updated with test code to ensure ongoing compatibility. This transition marks a shift towards greater long-term stability and security. Mastodon post celebrating the transition.
Looking Ahead
The year ahead brings exciting new opportunities as we build on our progress. Key priorities for 2024 / 2025 include:
Engaging
Community Engagement & Outward Communication: Enhancing collaboration with the Communication Working Group (CWG) and improving our public-facing communication around service status and outages.
Improving Documentation and Onboarding: We’ll enhance onboarding documentation and conduct dedicated sessions to help new contributors get involved in operations more easily. This includes improving the reliability and coverage of our testing processes, ensuring smoother contributions and reducing the learning curve for new team members.
Planning and Optimizing
Capacity Planning for Infrastructure Growth: As OpenStreetMap and the demand on our services grow, we will ensure we can scale to meet demand. By anticipating future needs and balancing performance with cost-effective growth, we aim to maintain the service quality and availability our community expects.
Ongoing Cost Optimisation: We’ll continue to find ways to reduce costs by leveraging sponsorships like the AWS OpenData programme, ensuring sustainable operations.
Continuing to Reduce Technical Debt: We will continue simplifying our infrastructure by reducing the maintenance burden of legacy systems, such as increasing the use of containers. This will help streamline management tasks and allow us to focus on other improvements, making the infrastructure more efficient and scalable over time.
Continue Infrastructure Improvements
Implementation of High Availability Load Balancers: Rolling out the HA (VRRP + LVS + DSR) configuration for load balancers to improve system reliability and reduce potential downtime.
Finalising Prometheus Integration with PagerDuty: Completing the integration of Prometheus for monitoring and PagerDuty for streamlined alerting and incident response.
Complete the Transition to Full Debian Environment: Migrating all remaining services from Ubuntu to Debian for increased stability and security.
Enhancing Disaster Recovery & Backup Strategies: Further refining our recovery documentation and introducing additional backup measures across critical services are protected and recoverable in the event of failure.